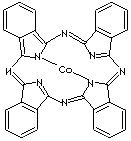
| COBALTOUS PHTHALOCYANINATE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 3317-67-7 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 222-012-7 | |
| FORMULA | C32H16CoN8 | |
| MOL WT. | 571.47 | |
| H.S. CODE | ||
| SMILES |
| |
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS | PcCo; Phthalocyanine cobalt(II) salt; | |
| Cobalt phthalocyanine; Phthalocyanine Cobalt; | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Phthalocyanine | |
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | purple powder | |
| MELTING POINT | ||
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.57 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Insoluble | |
| pH | 6 - 7 (2% Aq. Sol.) | |
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
| NFPA RATINGS | ||
| FLASH POINT |
| |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
| Phthalocyanine a macrocyclic compound. It consists of four isoindole-class [(C6H4)C2N] units linked by four nitrogen atoms to form a conjugated chain, which take play in hosting various different metal ions in its centrer. This structure is Macrocyclic structure shows a striking feature as a colorant like porphyrins (biopigments) in nature. Phthalocyanine derivatives derived from the basic compound of (C6H4C2N)4N4 are used as light-fast blue or green pigments. The hosted metals and substituted groups result in distinct colors; phthalocyanine (blue-green), copper phthalocyanine (blue), chlorinated copper phthalocyanine (green), and sulfonated copper phthalocyanine (green). Recently they are involved in the study of photosensitizer chemistry or metal complex chemistry such as transition-metal complex catalyst chemistry for uniform polymerization, luminescence chemistry and spectrophotometric analysis, organic synthesis and polymerization. Phthalocyanine pigments are used in enamels, linoleum, inks, plastics, and rubber goods. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
purple powder | |
|
DYE CONTENT |
98.0% min | |
|
Co CONTENT |
10.0% min | |
|
FREE Co CONTENT |
0.01% max | |
|
MOISTURE |
0.5% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||